In the rapidly evolving financial world, digital banking and payment infrastructures are continuously evolving. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the trends that are reshaping the industry and the opportunities they present.
We cover the emerging technologies and regulatory changes, so you can understand the forces driving transformation. Read on to equip yourself with the knowledge required to navigate this complex landscape and succeed in the financial services sphere.
- 1. Introducing Digital Banking
- 2. Exploring Top Trends in Digital Banking
- 3. Understanding the Payment Landscape
- 4. Analysing the Market & Identifying Opportunities
- 5. Setting Up the Core Banking System and Payment Infrastructure
1. Introducing Digital Banking
Overview, Statistics
What is digital banking? It refers to the provision of banking services via digital channels, e.g. websites, mobiles and other online platforms. It’s also a term that encompasses a wide array of services, such as account management, payments, transfers, loans, financial planning and investments – all accessible remotely through smartphones, laptops and PCs.
Digital banking represents a convenient option for customers, as it eliminates the need to visit a branch in person. This kind of service affords customers greater flexibility and accessibility when managing their finances.
Leveraging Remote Technology
Operating exclusively online, digital banks don’t provide physical branches. However, they still offer a wide array of banking services via digital channels. Due in part to reduced operational overheads, digital banks can offer customers competitive interest rates and lower fees, as well as innovative features like budgeting tools, automated savings and real-time transaction notifications.
As such, their benefits appeal to tech-savvy consumers looking for a convenient and cost-effective way to manage their money.
Increased Popularity & Adoption
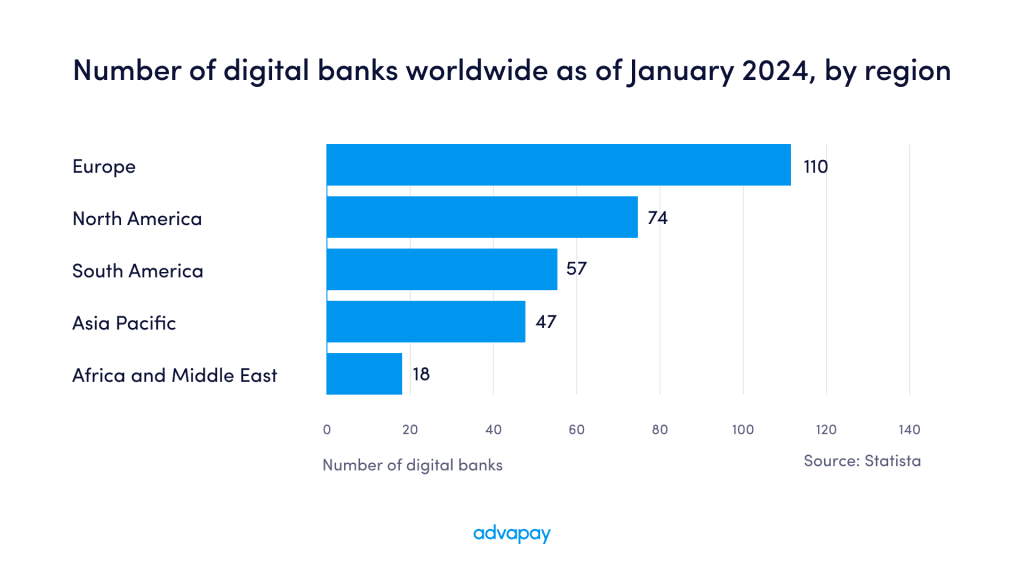
The benefits of digital banking have seen its popularity grow sharply in recent years, particularly in Europe, which has 110 digital banks – the highest number in the world (North & South America have 74 and 57 digital banks, respectively *see table below).
The digital banking platforms, also known as ‘Challenger banks’, ‘App-only banks’ and ‘online banks’, have seen their user base significantly expand, with some of the largest enjoying in excess of 100 million customers. Source: Statista.
The Key Components of Digital Banking
Here, we explore the essential elements that drive digital banking. Understanding these components highlights the profound impact digital banking has on modern financial services.
Mobile Banking Apps
Mobile banking apps have become ubiquitous, serving as one of the primary methods customers use to access their accounts, check balances, pay balances and move money on the go.
A recent Deloitte survey showed that 59% of customers use a banking app at least once a month, and the experience is enhanced through real-time notifications. Mobile banking is also viewed as a safe option thanks to innovative online security features like biometric authentication.
Online Banking
Another way customers can access online banking is via web-based portals. Customers can carry out various account transactions and manage their finances through a browser (e.g., Chrome or Safari) on an internet-connected smart device.
Digital Payments
The use of digital payments has exploded in recent years, particularly among Generation Z and millennial customers. As such, the adoption of P2P transfers, contactless payments, and mobile wallets has grown rapidly, thanks to their speed, security, and convenience. Whether used online or in-store, mobile apps allow for fast and secure transactions between individuals and businesses.
Fintech Integration
The integration of financial technology (fintech) solutions into digital banking platforms is reshaping the industry. Fintech startups are leveraging technologies like AI, data analytics and blockchain to drive innovation and enhance the experiences customers have.
Everything from robo-advisors to digital lending platforms, cryptocurrency wallets and personal finance management tools are changing the way people interact with money.
Growth Drivers
So, what is driving this rapid growth in digital banking? Let’s take a quick look at some of the fundamental factors behind the shift towards digital options.
- Changing Consumer Preferences – Customers are gravitating towards digital banking due to the increased flexibility and convenience it offers. Modern people lead busy lives, which often don’t give them time to visit a bank in person in the traditional way.
- More Advanced Features – Online banking features were once limited. However, technological advancements have allowed more sophisticated services to be provided, such as AI-driven chatbots, biometric authentication and personalized financial advice.
- Regulatory Initiatives – Regulatory bodies in the banking sector are also promoting digitalization through the introduction of initiatives like open banking and the adoption of standardized APIs that encourage innovation, competition and transparency.
The Importance of Digital Banking Businesses in the Digital Economy
Digital banking businesses and their importance to the digital economy shouldn’t be understated, as their role is pivotal to shaping the sphere and how it works. For instance, they have a crucial part to play in ensuring that underserved populations get access to banking services, such as savings accounts, payments and remittances.
As such, digital banking has extended its reach into previously untapped markets – something that empowers communities to participate more fully in the digital economy. Other vital contributions made by digital banking businesses include the following.
Driving Innovation & Efficiency
At the very heart of digital banking businesses is innovation – something that drives the development of new banking innovations, products and services. These advancements help digital banks to operate more efficiently and offer a smoother user experience.
Whether talking about AI-powered machine learning or blockchain, digital banks can use cutting-edge technologies to reduce their costs, streamline processes and remain competitive in a rapidly changing digital economy.
Enhancing Customer Experience
The customer experience is vital in the wider business world, and it’s no different in the digital economy. As they exist at the forefront of the sphere, it’s crucial for digital banking businesses to deliver seamless, personalized experiences to their customers.
The provision of intuitive mobile banking apps, responsive online platforms and proactive support allows the ever-evolving customer needs and expectations that exist in the digital world to be met.
Furthermore, enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty – created through more convenient access to innovative digital payment solutions and personalized financial advice – help to drive long-term growth and success.
Enabling Digital Transformation
Another way in which digital businesses are indispensable is the essential financial services and infrastructure they provide to companies undergoing digital transformation.
Whether enabling e-commerce transactions or facilitating digital lending and investment services, these businesses form the backbone of the digital economy, supporting the growth of organisations of all sizes.
By offering secure, reliable, and scalable banking solutions, digital banking businesses support firms in embracing digitalization and taking advantage of opportunities presented by the digital economy.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance
The digital economy is a highly regulated arena, which presents significant compliance challenges for businesses – especially in the financial services sector. As such, digital banking businesses need to navigate this complex landscape to remain compliant with laws governing data protection, money laundering, and cybersecurity.
The good news is that by investing in comprehensive compliance programs, implementing strict security measures, and staying abreast of regulatory developments, digital banking businesses can build trust with customers, regulators, and stakeholders – laying the foundation for sustainable growth and success in the digital economy.

2. Exploring Top Trends in Digital Banking
As we’ve already touched upon, the digital banking landscape is fast-paced and rapidly evolving. Driven by the need to stay ahead of the curve in terms of customer needs and expectations, the following trends are currently reshaping the sphere.
Trend #1 – An Increase in Contactless Payment Adoption
Contactless payment adoption has increased dramatically since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, social distancing wasn’t the only factor at play. Here, we take an in-depth look at the factors driving this trend, its impact on the banking sector and what the future holds.
Technological Innovations
Contactless payments wouldn’t even exist without the technological innovation that is Near Field Communication (NFC). It allows quick and secure transactions to be made simply by tapping a smartphone or debit-credit card near a payment terminal. Since the pandemic, it’s quickly become the payment method of choice for a large section of society.
Consumer Convenience
The act of paying contactlessly is a fast and convenient one. There’s no need to enter a PIN or sign for purchases under a certain amount, meaning that it’s one of the quickest and easiest ways to transact, and it’s something that appeals to modern consumers who want speed and efficiency.
A Freely Available Payment Option
Another driving factor behind the popularity of contactless payments is the fact that almost every retailer and service provider accepts them. Every customer is aware of the method and expects the option to be provided in an increasing number of settings.
Its popularity has also been accelerated by banks and financial institutions actively promoting mobile payment and contactless card solutions – something that’s further reinforced by incentives, like cashback and other rewards.
The Impact of Contactless Payments On the Banking Sector
The introduction of contactless payments into the digital economy has had a profound impact, not least being an intensification of competition among banks and fintech companies. These financial institutions and banks are investing heavily in new technologies and partnering with tech companies in order to get ahead and provide superior payment experiences for their customers.
Additionally, banks are increasingly integrating contactless payments in with their other banking services (such as combining payments with personalized offers and loyalty programs) to form a seamlessly unified and convenient service.
Trend #2 – Digital Wallets on the Rise
According to the 2024 WorldPay Report, $13.9 trillion was spent via digital wallets (a.k.a. e-wallets) in 2023, accounting for 50% of e-commerce and 30% point-of-sale consumer spend. This represents a remarkable surge in growth that’s being driven by changing consumer behaviors and increased need for convenient and secure payment solutions.
Come with us now as we take a detailed look at the impressive rise of digital wallets, why it’s happening and the wider implications for the banking industry.
The Key Drivers of Digital Wallet Adoption
At the centre of the surge in digital wallet adoption is the fact that over 80% of the world’s population owns a mobile phone. Modern smartphones are equipped with advanced capabilities like NFC as standard in the 2020s, making contactless payments available to many more people.
Other drivers of e-wallet adoption include:
- An Extensive App Ecosystem – It’s never been easier to access and use digital wallets, as there are hundreds available to download from Google Play and Apple’s App Store. These platforms are also simple to use and integrate smoothly with a variety of payment systems.
- The Development of Core Banking Systems – Core banking systems represent the backbone of a bank’s IT infrastructure and they’ve evolved significantly in the last few years. They enable banks and financial services companies to offer more sophisticated, secure, efficient and ultimately more appealing digital wallet services.
- Unparalleled Convenience – Digital wallets offer unparalleled convenient, allowing users to store multiple payment methods, loyalty cards and coupons, all in one place. Convenience ranks highly among the needs of modern consumers, and an e-wallet allows transactions to be completed with just a few taps – eliminating the need to carry physical cards.
Also, many of the approximate 26.5 million eCommerce retailers that exist online offer integrated digital wallet options. This makes it easy and convenient for users to buy goods and services without repeatedly having to enter their payment details.
- The Reassurance of Security – Digital wallets represent one of the most secure ways to store your money, using advanced security measures like encryption, tokenization and biometric authentication (facial & fingerprint recognition). This gives users the reassurance of knowing their funds are as safe as they can be.
- The eCommerce Boom – eCommerce has enjoyed a meteroic rise over the last decade. In 2014, global eCommerce retail sales sat at $1.3 trillion – a figure that’s expected to rise to $6.3 trillion in 2024. This has fueled the adoption of digital wallets to make paying for things online safer and more secure.

Trend #3 – The Mainstream Use of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency has come from nothing into mainstream use in the last fifteen or so years – a paradigm that has led to a significant and transformative trend in digital banking. What has driven this surge in uptake? Let’s take a look at the influencing factors.
Factors Driving Mainstream Cryptocurrency Adoption
The underlying technology of cryptocurrencies is blockchain, a decentralized system that’s known for offering transparency and security. The features on offer make it an attractive alternative to traditional banking services and its popularity is driven by a number of benefits.
- High Accessibility – At one time, cryptocurrencies were relatively difficult to access. However, technological advances have made them much more accessible to the average consumer. For instance, user-friendly apps like eToro and Coinbase have simplified the buying, selling and use of cryptocurrencies.
- Decentralization – A growing number of consumers prefer the freedom and lack of authority involvement in their investments – hence the increased interest in decentralized cryptocurrencies.
- High Return Investments – Compared to conventional investment opportunities, many consumers view cryptocurrencies as a lucrative investment opportunity. The potential for rapid, high returns has drawn individuals, retail and institutional investors into the market.
Regulatory Developments
For the first few years of its existence, crypto currency was self-governing – with a lack of central authority representing part of its appeal. However, some governments are beginning to recognize and regulate cryptocurrencies. This provides a legal framework that serves to boost consumer confidence in the sphere.
For example, Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) rules governing stablecoins are being introduced in mid-2024, with other MiCAR provisions coming into force on the 30th of December 2024. Also, additional guidance coming from global standard-setters like:
- the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO)
- the Financial Stability Board (FSB)
- the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- the Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
Despite these recommendations not carrying any current legal weight, they provide an important roadmap for national authorities to follow.
The Mainstream Acceptance of Cryptocurrencies
The development of CBDCs by various central banks reflects a growing acceptance that digital currencies are here to stay, and their aim is to combine the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability of traditional fiat currencies.
Prominent financial institutions like JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs, and PayPal have also started to offer cryptocurrency services, signalling a significant shift towards mainstream acceptance. Moreover, major corporations such as Tesla, Square, and MicroStrategy have invested heavily in cryptocurrencies, further legitimizing their use and acceptance.
The Impact of Cryptocurrency Adoption On the Banking Sector
The adoption of cryptocurrency is transforming the banking sector in a tangible way, introducing significant opportunities and having a major impact on how banks and financial institutions are choosing to operate.
- Augmented Services – In a move that cater to the growing demands of institutional and retail investors, banks are developing secure custody solutions for cryptocurrencies.
Also financial institutions are offering cryptocurrency services alongside their traditional services, allowing customers to buy, sell and manage cryptocurrencies directly from their current accounts.
- Competition & Innovation – The adoption of cryptocurrencies into the mainstream is causing more banks and other licenced financial institutions to collaborate with crypto companies to leverage their blockchain and crypto-technology expertise.
Industry innovation is also being encouraged, giving rise to a range of new financial products such as crypto-backed loans, interest-bearing crypto accounts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Trend #4 – ESG Compliance in Banking
Due in part to the energy-intensive nature of blockchain, adherence to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) rules have emerged as a crucial trend in digital banking. As a measure of commitment to eco-friendly practices, positive social impact and transparent governance, ESG principles are being integrated into banking operations, strategies and reporting.
Stakeholders are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, ethics, and transparency, and this trend is reshaping the banking sector, driving innovation, and enhancing stakeholder trust.
Factors Driving ESG Compliance
So, what is causing this shift towards ESG compliance? Two of the main drivers are investor demand and customer expectations. Firstly, institutional and retail investors are demanding that banks incorporate ESG guidelines into their business models – as ESG compliant banks are viewed as being less risky and more forward-thinking.
Consumers are also more conscious than ever about world issues like climate change and global injustice, and they expect the institutions they bank with to demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices and sustainability.
Mandated Regulatory Requirements
Another major reason behind the increased levels of ESG compliance in digital banking is one of necessity. Governments around the world are introducing regulations that mandate ESG reporting and compliance. For example, the EU’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulations (SFDR) requires that financial institutions to disclose their sustainability risks and impacts.
Global standards on ESG reporting are also being set by organizations like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). The aim is to encourage banks to follow these guidelines.
Reputational Risk Management
The banking sphere is like any other in that reputation matters, as it can have a major influence on a bank’s brand and customer loyalty. It’s a factor that causes digital banks to comply with ESG standards for fear of having their reputation damaged and losing trust with stakeholders.
The truth is that being ESG compliant can be a real differentiator in a very competitive market. Those who lead ESG initiatives are able to attract more clients and enjoy better business opportunities. Like it or not, sustainability and ethical operating matters to consumers, as evidenced by the increased popularity of green bonds and sustainable investment funds among customers seeking responsible investment options.
The Impact on the Banking Sector
As a result of this shift in the sector, banks are developing products that promote sustainability, e.g. green loans, renewable energy financing and eco-friendly credit cards. They’re also offering ESG-focused products, such as mutual funds and ETFs, which attract investors looking to align their portfolios with their values.
Other effects seen on the banking sector include:
- Carbon footprint reduction: Banks are taking steps to reduce their carbon footprint, such as sustainable procurement practices, implementation of paperless digital banking services and the use of energy-efficient buildings.
- Diversity & Inclusion: Moves to ensure ESG compliance are also driving banks to adopt inclusive practices, like the promotion of gender diversity in leadership, supporting community development initiatives and ensuring fair labor practices.
- Enhanced Reporting & Transparency: Banks are also adopting comprehensive ESG reporting frameworks that disclose their social, environmental and governance impacts in order to enhance transparency and stakeholder accountability.
- Data Analytics: Further reinforcing their commitment to transparency, banks are using digital and data analytics to accurately track and report their ESG metrics.
Trend #5 – Embedded finance
Another groundbreaking trend has emerged in the digital banking landscape – Embedded Finance. Fundamentally changing how financial services are delivered and consumed, it involves the integration of financial services into non-financial ecosystems and platforms. The result is a scenario in which consumers can seamlessly access banking services as part of their everyday lives.
Embedded finance is fundamentally reshaping the banking sector, offering opportunities for growth and innovation. So, let’s take a look at the driving forces, impacts and future ramifications.
The Drivers of Embedded Finance
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are at the center of the growth of embedded finance, as they allow the integration of financial services into a variety of different platforms. They facilitate communication and sharing of data between different types of systems, meaning that non-financial companies can offer financial services.
The innovation contribution of fintech companies is also playing a part in facilitating embedded finances. The new technologies they’re creating for payment processing, lending platforms and financial management tools are crucial to the existence of this growing trend.
Other drivers of embedded finance include:
- Customers expect a seamless experience: Modern consumers expect convenience in every aspect of their lives – including financial services. Embedded finance appeals to this demand by making financial services available on the platforms they already use each day, such as ride-sharing apps, social media and eCommerce websites.
- Personalization is also key: As part of the expected seamless experience, high levels of personalization are what draw people to embedded finance. It allows for financial services to be precisely tailored to specific needs and behaviors boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty as a result.
- The evolution of the embedded finance ecosystem: Also facilitating the adoption of embedded finance (EF) is the rapid evolution of the technology found in EF platforms. This is as a direct result of the increased collaboration between fintech companies and traditional financial institutions.
At the outset, Open Banking ushered in a new type of collaboration between financial services entities and more convenient payment options. By enabling third-party developers to access financial data through secure APIs, open banking dismantled the traditional barriers between financial institutions and fintech companies.
Since then, embedded finance has come to include a broad array of financial services such as lending, insurance, and investment products embedded directly into various digital ecosystems. APIs and open banking frameworks enable non-financial platforms to offer sophisticated financial services without needing to develop the infrastructure themselves.
The Impact on the Banking Sector
Embedded finance lets digital banks reach customers beyond their traditional channels, meaning that they can tap into new customer segments and geographies. It’s also now possible for banks to generate new revenue streams via fee-based services provided through partner platforms such as payment processing, insurance and lending.
The virtuous effect on the customer journey is palpable as this new landscape offers unprecedented levels of convenience where it’s needed the most. For example, a car buyer can obtain a loan directly through a dealership’s website or make payments through a ride-sharing app without leaving the platform.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction & Operational Efficiency
Furthermore, the data leveraged from non-financial platforms allows banks to offer evermore tailored financial services and products, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This is reinforced by the streamlining of payment, lending and account management processes that third-party platform integration provides – something that also serves to reduce operational costs for the provider.
The vast amounts of data generated by embedded finance integration on partner platforms lead banks to enjoy better risk management, customer insights and fraud detection.
3. Understanding the Payment Landscape
Key Players Shaping the Digital Banking Industry
In this section, we delve into the key players revolutionizing the payment landscape and examine how these entities are shaping the future of digital payments.
Key Player #1 – Traditional Banks & Financial Institutions
Traditional banks and financial institutions are the foundation of the digital banking industry, providing a range of conventional banking services such as deposits, loans, and wealth management.
While they may have initially faced challenges adapting to digitalization, many traditional banks have since embraced technology to offer online banking platforms, mobile apps, and digital payment solutions to their customers.
These institutions leverage their extensive infrastructure, regulatory expertise, and customer trust to stay competitive in digital banking. Banks play a central role in providing payment and digital banking services.
Through banks, other licensed financial services companies (such as e-money institutions, payment institutions, MSB companies, and fintech firms) can access the payment infrastructure. The range of services these regulated payment companies can offer varies by jurisdiction and company type, but it is generally more limited compared to banks. For example, European e-money and payment institutions can only connect to SEPA through banks (or CENTROLINK by the Bank of Lithuania) and need to use banks to safeguard client funds.
Key Player #2 – Fintech Startups
Fintech startups have emerged as disruptive forces in the digital banking industry, leveraging technology to offer innovative financial products and services.
From digital-only banks and peer-to-peer lending platforms to robo-advisors and blockchain-based payment solutions, fintech startups are reshaping traditional banking models and challenging established players.
These agile and tech-savvy startups often prioritize customer experience, flexibility, and accessibility, attracting tech-savvy consumers and driving competition in the industry.
Key Player #3 – Payment Service Providers
Payment service providers (e.g. e-money and payment institutions, MSB companies and other fintech companies) play a crucial role in facilitating digital transactions and enabling seamless payments across various channels.
These providers offer a wide range of payment solutions, including merchant services, payment gateways, digital wallets, and mobile payment apps. By offering secure, convenient, and cost-effective payment solutions, payment service providers drive the adoption of digital payments and support the growth of e-commerce and online businesses.
Key Player #4 – Currency Exchange Providers
Currency exchange providers specialize in facilitating foreign exchange transactions and currency conversions for individuals and businesses. In the digital banking industry, these providers offer online platforms and mobile apps that enable customers to exchange currencies, transfer funds internationally, and manage forex transactions efficiently.
Offering competitive exchange rates, low fees, and fast processing times, currency exchange providers allow businesses to conduct cross-border transactions and expand their global reach.
Key Player #5 – Regulatory Bodies & Compliance Providers
Regulatory bodies and compliance providers also play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity, security, and stability of the digital banking sector. These regulatory bodies set standards, guidelines, and regulations governing financial services to protect consumers and prevent fraud.
Compliance providers offer solutions and services that help banks and financial institutions adhere to regulatory requirements, manage risk, and mitigate compliance-related challenges in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Regulatory Landscape & Compliance Requirements in the Digital Banking Industry
As digital banking continues to evolve and expand, regulatory bodies around the world are tasked with overseeing the industry and enforcing compliance with relevant laws and regulations. We now explore the regulatory landscape and compliance requirements that digital banking businesses must navigate to operate successfully in this highly dynamic environment.
The Regulatory Bodies That Exist
A number of different entities can be described as regulatory bodies in the digital banking sphere. Let’s examine the institutions involved in overseeing the sector.
- Central banks play a pivotal role in regulating the banking industry and overseeing monetary policy. They establish guidelines and standards for banking operations, monitor systemic risks, and supervise financial institutions to maintain financial stability and promote economic growth.
- Financial Regulators, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the USA and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, are responsible for overseeing specific aspects of the financial services sector, such as securities trading, investment management, and consumer protection.
These regulators enforce regulations, investigate misconduct, and impose penalties for non-compliance to ensure market integrity and investor confidence.
- Data Protection Authorities. In an era of increasing data breaches and privacy concerns, data protection authorities enforce laws and regulations related to the collection, storage, and processing of personal and financial data.
Entities operating in the digital banking industry must comply with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States to safeguard customer information and mitigate data security risks.
Compliance Requirements for Digital Banking Businesses
So, what do regulators expect from anyone operating in the digital banking sphere? The following represent the primary compliance requirements that digital banking businesses must adhere to.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations
AML regulations aim to prevent money laundering and the financing of terrorist activities by imposing obligations on financial institutions to identify and report suspicious transactions, conduct customer due diligence, and implement robust AML compliance programs.
Digital banking businesses must adhere to AML regulations to mitigate the risk of illicit financial activities and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Know Your Customer (KYC) Requirements
KYC requirements mandate that financial institutions verify the identity of their customers, assess their risk profiles, and monitor their transactions to prevent fraud, identity theft, and other illicit activities. Digital banking businesses must implement KYC procedures to authenticate customer identities, validate their information, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Cybersecurity Standards
Cybersecurity standards govern the security measures and protocols that financial institutions must implement to protect sensitive data, systems, and infrastructure from cyber threats and attacks.
Digital banking businesses must comply with cybersecurity regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the ISO/IEC 27001 standard to safeguard customer information, prevent data breaches, and maintain the integrity of their digital platforms.
4. Analysing the Market & Identifying Opportunities
Understanding market dynamics is crucial for success. Here, we delve into market analysis, exploring market size and growth trends. By identifying opportunities, businesses can strategically position themselves for expansion and innovation.
Market Size and Growth
The digital banking market is projected to grow from USD 107.67 billion in 2024 to USD 199.38 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.01% during the forecast period (2024 – 2032). For reference, the digital banking market was valued at $98.6 billion in 2023.
Additionally, the market size of digital banking platforms in 2023 was $25.18 billion, a figure that’s projected to rise at a CAGR of 20.9% to $138.96 billion by 2031. Studies have also shown that the fastest-growing is the Asia-Pacific market, with the largest being in North America.
Identifying Opportunities for the Digital Banking Industry
Digital banks must strive to implement strategies to capitalize on the strong growth in the sector. By leveraging market insights and technological advancements, digital banks can capitalize on emerging trends and drive future success. The following illustrate some of the biggest opportunities in today’s digital banking industry.
Personalized Banking Services
In an age where personalized experiences are king, digital banking businesses have the opportunity to attract new customers through the provision of tailored banking services that cater to the unique needs and preferences of each individual.
By leveraging data analytics, AI, and machine learning, digital banks can gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and financial goals. This information allows them to offer personalized recommendations, products, and services that enhance customers’ overall banking experience.
Embracing Embedded Finance
As we spoke about earlier, the convergence of finance and technology has given rise to embedded finance, where financial services are seamlessly integrated into non-financial platforms and ecosystems. The opportunity exists for payment providers to capitalize on this trend by partnering with ride-sharing apps and eCommerce platforms.
The frictionless payment experiences that exist within these platforms allow providers to capture a share of transaction volumes and tap into new customer segments, driving revenue growth and customer engagement.
Seamless Digital Payments
The rise of e-commerce and online transactions presents a significant opportunity for digital banking businesses to innovate in the realm of digital payments. By offering seamless and secure payment solutions, digital banks have the chance to meet the growing demand for choice and convenience to capture a larger share of the digital payments market.
Whether through mobile payments, peer-to-peer transfers, or contactless transactions, digital banking businesses can streamline the payment process and enhance the customer experience.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Solutions:
During 2023, ransomware attacks targeting the financial sector rose from 55% to 63%, highlighting the increased prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches. As such, there is a growing demand for robust cybersecurity solutions in the digital banking industry.
Digital banking businesses have the opportunity to differentiate themselves by investing in advanced cybersecurity measures that protect customer data, secure digital transactions, and safeguard against cyber-attacks. This helps to build customer trust, mitigate risks, and demonstrate a commitment to data security and privacy.
The Integration of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and biometrics also present exciting opportunities for innovation in the digital banking industry.
By harnessing the power of these technologies, banks can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and deliver new and innovative services to customers. Whether through blockchain-based payment solutions, AI-powered chatbots, or biometric authentication systems, digital banking businesses can stay ahead of the curve and be at the cutting edge of innovation in the industry.
Market Niches and Underserved Segments
One of the most significant opportunities for the digital banking industry lies in promoting financial inclusion. Millions of individuals worldwide lack access to traditional banking services, presenting a vast untapped market for digital banking solutions.
By offering mobile banking apps, digital wallets, and other innovative products, digital banking businesses can reach underserved populations and new niches, empower them with access to financial services, and drive financial inclusion on a global scale.
Identifying potential market niches or underserved segments within the digital banking industry can lead to increased revenue. By conducting market research, digital banks can understand the needs, preferences, and pain points of specific demographic groups or customer segments.
Opportunities to target market niches and underserved segments include:
- Banking services tailored to specific demographics (e.g., millennials, Gen Z, seniors)
- Banking services tailored to specific geographical areas (e.g. for African countries)
- Specialty banking services for underserved communities or niche industries (e.g., freelancers, gig economy workers, small businesses)
- Ethical or sustainable banking options for environmentally conscious consumers
- Digital banking solutions with a focus on financial wellness, education, or empowerment
- Targeted banking services for specific life stages or events (e.g., student banking, retirement planning)
Competitive Analysis & Market Differentiation
Understanding competitive dynamics is crucial in the rapidly evolving digital banking sector, as it informs digital banks on how they can differentiate themselves. As such, there are a number of ways that digital banking businesses can stay ahead of the competition.
- Assessing competitors’ offerings within identified market niches or underserved segments.
- Identifying gaps or areas for improvement in their existing digital banking solutions.
- Developing a value proposition and differentiation strategy to stand out in the market and attract target customers.
- Leveraging technology, innovation, and customer-centric approaches to differentiate your digital banking offerings.
Continuously monitoring market trends and customer feedback allows banking businesses to adapt their strategies to offer something uniquely appealing and maintain a competitive edge.
Regulatory Considerations
Naturally, understanding the regulatory framework of the financial segments that banks are targeting is key to capitalizing on the opportunities that exist. As such, here’s a selection of the regulatory considerations that need to be made by digital banking businesses.
- It’s important to understand regulatory requirements and compliance standards specific to the identified market niches or underserved segments.
- It’s also necessary to obtain the appropriate licences, registrations and/or permissions (e.g. E-money/payment institution licence, MSB registration, registration as an agent under the BaaS scheme)
- Digital banking providers must ensure that their digital banking services comply with relevant regulations, including consumer protection laws and data privacy regulations.
In order to navigate what is often a complex regulatory landscape, digital banking businesses should consult with legal and regulatory experts with a view to mitigating compliance risks.
5. Setting Up the Core Banking System and Payment Infrastructure
Any digital banking business wanting to provide financial services like IBANs, SEPA/SWIFT payments, payment cards, or currency exchanges must have a system equipped to handle these functions. This entails having a fully operational core banking system, completing the necessary legal preparations, and connecting the system to financial services and other providers. When it comes to linking up with the payment and banking infrastructure, you have two viable options:
Option #1 – Developing a payment infrastructure independently
This path entails forging business partnerships and constructing integrations, which demands considerable expertise in both fintech business development and banking/payment technologies.
To offer standard payment services like IBANs, currency exchange & payments, and card issuance, collaboration with banks and payment service providers is a must. If you aim to issue your own IBANs, you’ll need to join the SEPA network and acquire a Bank Identification Code (BIC) from SWIFT.
Check out our comprehensive guide on this topic [link]. Similarly, if you intend to issue your own cards, becoming a principal card issuer with Visa or Mastercard is essential.
Option #2 – Engage a Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Provider
The less complex route is to engage with a BaaS provider who can furnish digital banking businesses with a pre-configured infrastructure. Leveraging Core Banking software such as Macrobank, which is primed for integration with a BaaS provider, it’s possible to expedite the process. This allows you to make use of a range of pre-built services and solutions, streamlining your entry into the financial services landscape.
Establishing Partnerships with Banks & Other Payment Service providers
Establishing strategic partnerships with traditional banks, other financial services companies, and payment networks has become essential for digital banks in providing comprehensive services and access to a ready infrastructure.
Such collaborations facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements, improve service delivery, and enable digital banks to leverage established trust and customer bases, driving growth and innovation.
What digital banks get from these partnerships
So, what, more specifically, do digital banks get from establishing these partnerships? Firstly, they get access to ready banking and payment service infrastructure – negating the need to build their own from scratch (something that can take years, plus significant investment).
This infrastructure allows digital banks to offer a wide range of banking and payment services, including current accounts, card issuing, currency exchange and IBANs.
It also allows a banking partner’s established regulatory compliance to be leveraged, meaning the risks associated with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, and data security standards are mitigated.
The Benefits of Connecting to a Ready Infrastructure
When connecting to a ready payment and banking infrastructure there are a variety of advantages that can be enjoyed. They include:
- API Integration: Banks and payment networks offer application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable digital banks to integrate seamlessly with their systems, allowing for real-time access to account data, transaction processing, and payment authorization.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Partnering with banks and payment networks also provides digital banks with a scalable and flexible infrastructure that can accommodate growth in customer base, transaction volume, and product offerings. All this is possible without the need for significant upfront investment in infrastructure development.
- Time-to-Market: By leveraging the existing infrastructure of banking and payment partners, digital banks can accelerate their time-to-market and launch innovative financial products and services more quickly, gaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape.
Selecting the Right Payment Technology & Core Banking Platforms
When choosing the right core banking system for your institution, there are several crucial factors that need to be considered to ensure it aligns with your business goals and operational requirements. Here are some key aspects to take into account:
- Scalability: It’s important that the core banking system in question can scale with your institution’s growth. It should be able to accommodate for an increasing number of customers, transactions, and products/services without compromising on your performance or reliability.
- Flexibility & Customization: You should also look for a core banking system that allows customization to meet your unique needs and regulatory requirements. Flexibility in configuration and workflow management is essential to adapt to changing business processes and market conditions.
- Integration Capabilities: You also need to assess the system’s ability to integrate with banks, financial services providers, third-party applications, regulatory compliance tools, and other systems within your IT infrastructure.
APIs and open architecture are crucial for easy integration and interoperability, so check if your core banking system provider offers prebuilt integrations with different financial and other service providers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Also ensure that the core banking system complies with the relevant regulatory standards and requirements in your jurisdiction. It should support compliance with anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC), data protection, and other regulatory frameworks.
- Security Features: Security is paramount in banking operations. Therefore, it’s vital to evaluate each core banking system’s security measures. This includes aspects like data encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, audit trails, and compliance with industry standards such as GDPR and AML.
- User Experience: A user-friendly interface and intuitive workflow are essential for efficient operations and customer satisfaction, meaning that the core banking system you choose should offer a seamless user experience for both staff members and customers, with easy navigation and accessibility across devices.
- Reliability and Performance: Any core banking system worth choosing should be highly reliable, with minimal downtime and robust disaster recovery mechanisms in place. It should also demonstrate high performance to handle peak transaction volumes and maintain responsiveness under load.
- Support and Maintenance: Be sure to check out the vendor’s track record in providing ongoing support, software updates, and maintenance services. Timely support and regular updates are crucial in addressing issues, enhancing functionality, and remaining compliant with evolving regulations.
- Cost and Total Ownership: Naturally, it’s important to know the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the core banking system, including initial implementation costs, licensing fees, ongoing maintenance, support, and training expenses. Consider both short-term and long-term costs to ensure it’s affordable and sustainable.
- Vendor Reputation and Stability: Lastly, you should go for a reputable vendor with a proven track record in delivering core banking solutions and serving financial institutions of similar size and complexity. Consider the vendor’s financial stability, industry expertise, and customer satisfaction levels, the best for which is through references and reviews.
Advapay at stake:
How can Advapay can assist you in launching your fintech business?
• Assistance in EMI/PI licencing in the EEA/UK
• Registration of MSB company in Canada
• Delivery of a comprehensive Core banking system encompassing back-office and white-label applications for end-users
• Assistance in payment infrastructure development
• BaaS-solutions in collaboration with our partners – EEA/UK licenced EMIs and PIs