In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the banking sector is experiencing a profound transformation driven by technology. Among the many innovations reshaping the industry, Banking APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are a powerful tool driving efficiency, accessibility, and innovation in financial services.
Banking and financial service APIs facilitate smooth integrations among diverse financial systems and applications. APIs enable fintech companies to link their platforms with various banking systems, payment gateways, and third-party services by offering standardised communication and data exchange methods. This seamless integration empowers businesses to enhance services, streamline operations, and provide a superior user experience.
With the aid of Bank APIs, third-party financial and non-financial institutions can deliver financial services without needing to develop their own payment infrastructure or obtain a license. APIs act as catalysts for innovation in the fintech sector. They allow fintechs to utilise existing infrastructure and build upon it rather than start from scratch. With APIs and core banking systems like Macrobank, fintech startups and established entities can swiftly develop and deploy new solutions, products, and services. This agility fosters the development of innovative financial tools like digital wallets, robo-advisors, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and more.
- What Is Banking API?
- How Banking APIs Operate
- Two main types of Banking APIs
- Key Advantages of API Banking for Fintech Companies
- How to start your fintech company or digital bank with the assistance of banking APIs
- Banking APIs functions and examples
- APIs banking platform
- The Future of Banking: A Unified Digital Landscape
What Is Banking API?
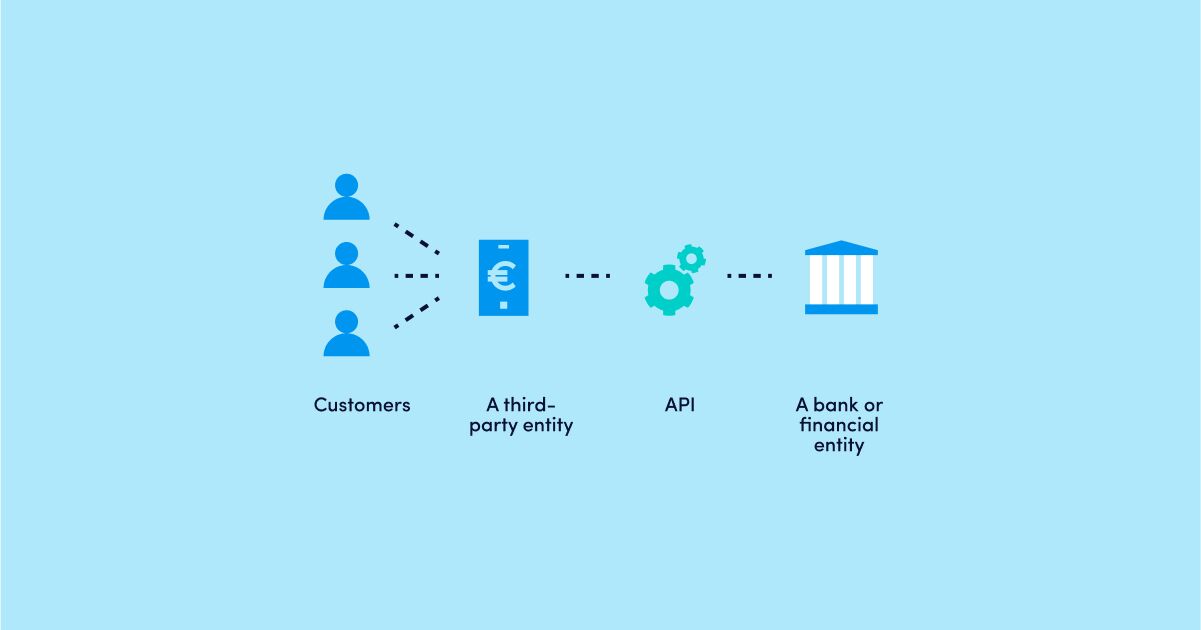
Banking APIs, short for application programming interfaces, serve as a bridge for seamless data transfer between two entities.
These APIs empower third-party entities (financial or non-financial institutions) to access banking services offered by financial institutions or extend those services to other entities. Fintech companies utilise API banking protocols to integrate diverse services and provide streamlined solutions to their customers.
From a technological perspective, it’s a bridge that connects core banking software systems like Macrobank (a system implemented for a third-party entity) with the infrastructure of a bank or a financial institution, allowing them to communicate and share data securely. An API, or Application Programming Interface, comprises a set of rules, protocols, and tools enabling core banking software solutions to communicate and execute various tasks.
APIs enable third-party financial and non-financial institutions to provide various financial services through their applications or platforms. Before any technological integrations, these third-party institutions must establish agreements with banks or financial institutions that are Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) providers, that are willing to share their APIs.
How Banking APIs Operate
In the framework of Banking APIs, a third-party financial or non-financial entity establishes a connection to a bank or financial institution (BaaS-provider) system via the API. Bank APIs enable communication and data exchange between different software systems and allow authorised entities to access banking data and functionality securely, enabling a wide range of services.
The bank or financial institution grants restricted and secure access to its payment infrastructure, allowing third-party entities to retrieve data and perform various banking functions such as account opening, transactions, verification, validation, balance inquiries, and more.
Typically, BaaS providers offer APIs rather than complete back-office systems to third-party entities. That means these third-party entities must possess a core banking platform to integrate the APIs BaaS providers provide.

Two main types of Banking APIs
There are two types of banking APIs that cater to different needs and purposes within the financial industry.
Open Banking or Open Banking APIs
Open Banking APIs are designed to provide third-party providers (TPP) access to customer data through open APIs, fostering innovation and competition in the financial services sector.
The concept of open banking surged in popularity in 2015, marked by adopting a new payment services directive by the European Parliament, PSD2. This directive mandates European Union and UK banks to grant third-party access to customer data through open APIs. Third-party entities can securely access customer bank account data, subject to customer approval. This framework empowers non-bank institutions to develop value-added services leveraging banking data and the ecosystem.
A common application of the open banking API involves consolidating data from multiple bank accounts into a unified view within the TPP application. There are two primary types of TPPs: Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs), which link to a customer’s account to initiate payments on their behalf, and Account Information Service Providers (AISPs), which connect to a customer’s bank account to offer financial services like money management.
Banking as a Service (BaaS) or Partner APIs
Partner or BaaS APIs are developed through collaborations between banks and third-party partners, enabling expansion into new channels or utilising innovative products. An example is a scenario where a fintech firm lacking its own payment infrastructure establishes a connection with a bank’s infrastructure via API. Through this connection, the fintech company can offer services such as opening current accounts, facilitating payments, and managing currency transactions.
Key Advantages of API Banking for Fintech Companies
API banking offers fintech companies many benefits that are pivotal in today’s digital financial landscape.
Firstly, it provides seamless integration with banking systems, allowing fintechs to access various financial services and data without needing extensive infrastructure development or their own financial services licence. This accelerates time-to-market for new products and enables greater innovation and agility. API banking empowers fintechs to disrupt the financial industry, driving growth, efficiency, and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving digital economy.
So, what are the primary benefits of API Banking for Fintech Enterprises?
1. Fast-to-market
Speed up time-to-market by tapping into pre-existing payment infrastructure. This eliminates the need to build payment systems and obtain a financial services licence from scratch.
2. New revenue streams
Promotes collaboration and partnerships between fintechs and traditional/licenced financial institutions, unlocking new revenue streams and expanding market reach.
3. Regulatory adherence
Banking APIs are crafted to adhere to rigorous regulatory standards, prioritising high security. This ensures third-party financial service providers can utilise compliant services aligned with regulatory requirements.
4. Enhanced customer experience by facilitating personalised and streamlined financial services
APIs enable banks and financial services to offer a more personalised and tailored customer experience. By integrating with banks, fintech companies can offer customers a wider range of options and functionalities.
5. Facilitated data accessibility
With the help of a core banking system (e.g., Macrobank by Advapay), APIs provide seamless communication between the bank system and the third-party provider’s system. APIs are vital in exchanging, extracting and presenting customer, payment, account and other data.
Open Banking APIs have opened up a new frontier of data accessibility, allowing the creation of thousands of apps and innovative financial services through secure connections to consumer-permission data.
How to start your fintech company or digital bank with the assistance of banking APIs
To kickstart your fintech venture as a digital bank utilising banking APIs, there are several crucial steps to follow.
1. Conduct research
Firstly, conduct thorough research to pinpoint the specific niche or target market you intend to serve within the digital banking landscape. During this phase, outline the payment services you plan to offer.
2. Meet regulatory requirements
Additionally, prioritise compliance with regulatory frameworks governing the financial industry to ensure legal adherence. Obtain the necessary e-money, payment licenses or registrations as mandated.
3. Establish partnerships
Next, establish partnerships with banks and other financial services institutions that provide API access, ensuring alignment with your business model and needs.
4. Choose core banking platform
Then, develop or select a ready core banking platform such as Macrobank by Advapay, where your Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) partners (banks or other financial services providers) will be linked through APIs. This platform allows for integrating various providers, enabling you to build a system that aligns with your business objectives.
Through strategic planning, partnerships, and technological innovation, launching your fintech company as a digital bank with banking APIs can pave the way for success in the competitive financial services sector.
Creating a fintech company or digital bank involves strategic decisions, partnerships and technological developments. Advapay enables the swift creation and launch of digital banking and payment products, allowing our clients to establish a neobank with pre-built modules and integrations. Leveraging Advapay’s Core banking software removes the need to develop core banking and basic fintech modules internally, thus reducing costs and accelerating the launch process. However, a fintech, e-money, payment or MSB license is still required to distribute financial services.
Banking APIs functions and examples
Here, we outline a typical combination of a digital bank’s proprietary and third-party APIs to commence business operations effectively:
Core Banking System (CBS)
A fintech company or digital bank can utilise a ready-core banking solution equipped with APIs to manage essential functions, including account management, transaction processing, currency exchange, etc.
Customer Onboarding
APIs facilitate crucial aspects of customer onboarding, such as identity verification and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks, by integrating with third-party services specialising in these areas, like Sumsub, Veriff, iSpiral, Ondato and Shufti Pro.
Payment Infrastructure
Fintech companies can integrate with payment services providers, currency exchange providers like Currency Cloud and Convera, payment processors and gateways via APIs to manage electronic transactions and facilitate international transfers using ready services.
Payment cards
Third-party card issuing services like Wallester or Decta enable digital banks to issue physical or virtual debit/credit cards and manage card-related functionalities efficiently.
Additional Financial Services
APIs are leveraged for offering lending, investment or insurance products through integration with third-party platforms.
Customer Engagement and Support
Digital banks can integrate AI-driven chatbots for customer queries and offer personal financial management tools for expense tracking and budgeting through third-party APIs or proprietary solutions.
Security
APIs assist in real-time fraud detection and multi-factor authentication implementation to bolster banking applications’ security.
Data Analytics and Insights
Integration with analytics platforms enables digital banks to gain insights into customer behaviour and optimise operations effectively.
APIs banking platform
Advapay’s core banking Platform, Macrobank, is a scalable solution for designing various payment products for e-wallets, neobanks, and money transfer systems. This platform integrates complex financial services providers based on an API-based architecture.
The API-centric approach enables rapid time-to-launch and facilitates market expansion with Advapay’s Platform in a short period. The software offers pre-built integrations (APIs) with various service providers, including IBAN and payment providers, currency exchange platforms, card issuers, and AML/KYC service providers, thereby reducing time-to-market.
Advapay’s core banking Platform, Macrobank, provides the following features:
- Multicurrency accounts
- Payments and transfers
- Currency exchange
- Card issuing
- Onboarding & KYC/AML module
- Tariffs and fees
- Financial Accounting
- Wide range of customisation & setting features
- Workflow manager
- and more
The Future of Banking: A Unified Digital Landscape
In the dynamic evolution of the banking sector, the emphasis on cohesive digital platforms and accessible APIs is poised to grow even stronger. Banks acknowledge the importance of maintaining flexibility and responsiveness to evolving customer demands and market trends.
By adopting these strategies, banks can position themselves as pivotal entities in a digital environment that seamlessly integrates financial services, technology, and innovation.
Banks and other licenced entities like e-money or payment institutions will collaborate with third-party fintech firms and service providers to offer customers various financial solutions within this framework.
API accessibility will empower banks to harness the expertise and capabilities of these external partners, enabling the delivery of pioneering products and services that align with the changing preferences of their clientele.
Advapay at stake:
How can Advapay can assist you in launching your fintech company with the help of Banking API or any other financial institution API?
• Delivery of a comprehensive Core banking system encompassing back-office and white-label applications for end-users with ready integrations
• Assistance in payment infrastructure development
• BaaS-solutions in collaboration with our partners – EEA/UK licenced EMIs and PIs
QA
Banking APIs, short for application programming interfaces, serve as a bridge for seamless data transfer between two entities.
A third-party financial or non-financial entity establishes a connection to a bank or financial institution (BaaS-provider) system via the API.
There are two types of banking APIs that cater to different needs and purposes within the financial industry:
– Open Banking or Open Banking APIs;
– Banking as a Service (BaaS) or Partner APIs.
1. Fast-to-market
2. New revenue streams
3. Regulatory adherence
4. Enhanced customer experience by facilitating personalised and streamlined financial services
5. Facilitated data accessibility
1. Conduct research
2. Meet regulatory requirements
3. Establish partnerships
4. Choose core banking platform
1. Core Banking System (CBS)
2. Customer Onboarding
3. Payment Infrastructure
4. Payment cards
5. Additional Financial Services lending, investment or insurance
6. Customer Engagement and Support
7. Security
8. Data Analytics and Insights
Core banking Platform (e.g. Macrobank) provides the following features:
1. Multicurrency accounts
2. Payments and transfers
3. Currency exchange
4. Card issuing
5. Onboarding & KYC/AML module
6. Tariffs and fees
7. Financial Accounting
8. Wide range of customisation & setting features
9. Workflow manager
and more