Banking as a Service (BaaS) is a financial industry concept that integrates banking and financial services into financial or non-banking platforms through application programming interfaces (APIs). Essentially, BaaS allows third-party companies, often fintech firms or other businesses, to offer banking and financial services to their customers without having to build and maintain their banking and payment infrastructure from scratch and without owning a financial services licence.
Banks or other licenced financial services companies provide various financial products and services, such as current accounts, payment processing, currency exchange, cards, AIS, PIS and more. BaaS can offer these services as white-labelled or embedded services in other applications or platforms. This opens up new possibilities for innovation and additional money streams.
This article discusses the world of BaaS, exploring its vast opportunities and advantages to traditional financial institutions and innovative startups.
Content
- Opportunities for Fintech Startups
- Opportunities for established financial services businesses
- Opportunities for BaaS providers
- Opportunities for customers
- What is a BaaS example?
- Key characteristics and benefits of Banking as a Service
- Evolution of BaaS
- Types of BaaS or Embedded Finance services
- What is the difference between Banking as a service and Open banking
- How to Get Started with BaaS
Opportunities for Fintech Startups
BaaS opens up many opportunities for fintech startups and emerging players in the financial industry. By partnering with BaaS service providers, these startups can focus on innovation and developing customer-centric financial solutions rather than navigating the complexities of developing a payment infrastructure independently or becoming a licenced bank or financial institution. BaaS allows for faster market entry, enabling fintech startups to launch their products and services without extensive delays, thus gaining a competitive edge.
Opportunities for established financial services businesses
For established and licenced fintech businesses, leveraging Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers many exciting opportunities to enhance their existing offerings and stay at the forefront of digital innovation. By collaborating with BaaS providers, these businesses can expand their product and service offerings without investing significant resources in building their banking and payment infrastructure.
BaaS enables different companies to integrate financial functionalities, such as different payment methods, accounts, and cards directly into their core banking platforms. Newly integrated products offer customers new services and generate new revenue streams. Ultimately, embracing BaaS empowers established businesses to adapt swiftly to the market’s ever-changing demands and leverage financial services’ power to drive growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term success.
Opportunities for BaaS providers
For Banking as a Service (BaaS) providers, there are abundant opportunities to share their services with other companies, fostering mutually beneficial collaborations. By offering their robust banking or payment infrastructure and financial capabilities through APIs, BaaS providers can unlock new revenue streams and expand their customer base.
Additionally, it generates a vast market of potential partners and clients, enabling BaaS providers to establish themselves as key players in the rapidly evolving financial ecosystem.
Moreover, as BaaS gains prominence, partnerships with diverse businesses create opportunities for cross-industry innovation, resulting in novel financial solutions and services that cater to a broader range of customer needs. Embracing this collaborative approach drives business growth and accelerates innovation in the financial sector, ultimately shaping the future of banking and customer-centric financial services.
Opportunities for customers
Leveraging Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers customers exciting opportunities, revolutionising how they interact with financial services. BaaS enables customers to access different banking products and services through their favourite platforms and applications.
Integrating BaaS solutions into various industries, such as e-commerce and travel, also means customers can enjoy personalised financial experiences tailored to their needs.
Moreover, BaaS fosters a competitive market environment, encouraging financial providers to offer better rates, a broader portfolio of services and innovative solutions to attract and retain customers.
What is a BaaS example?
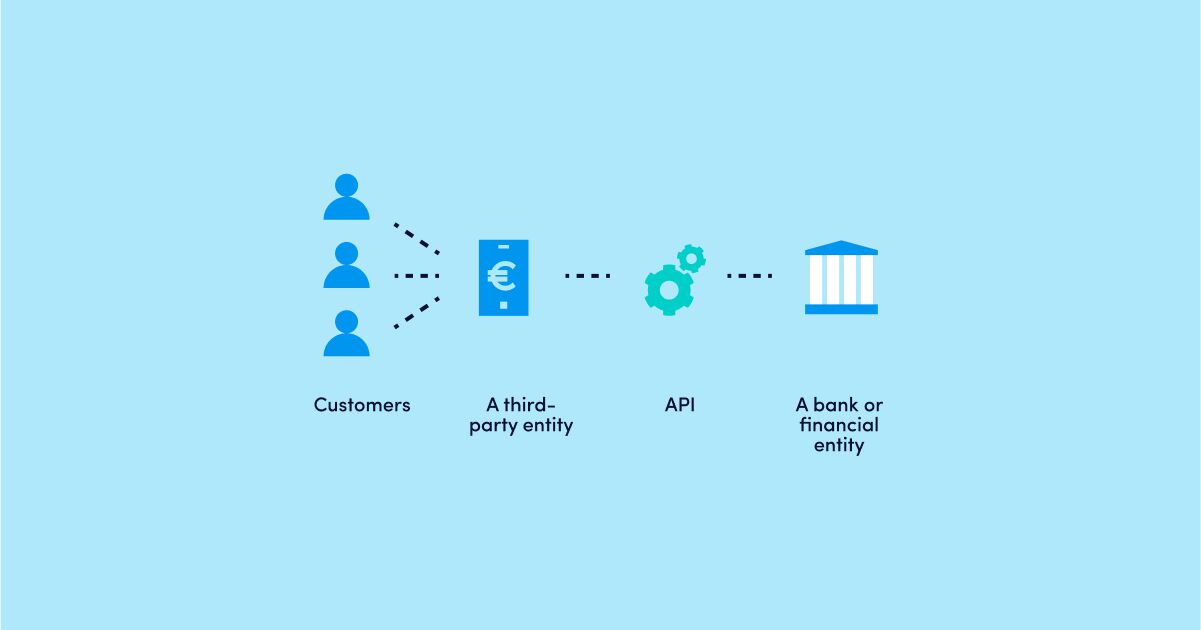
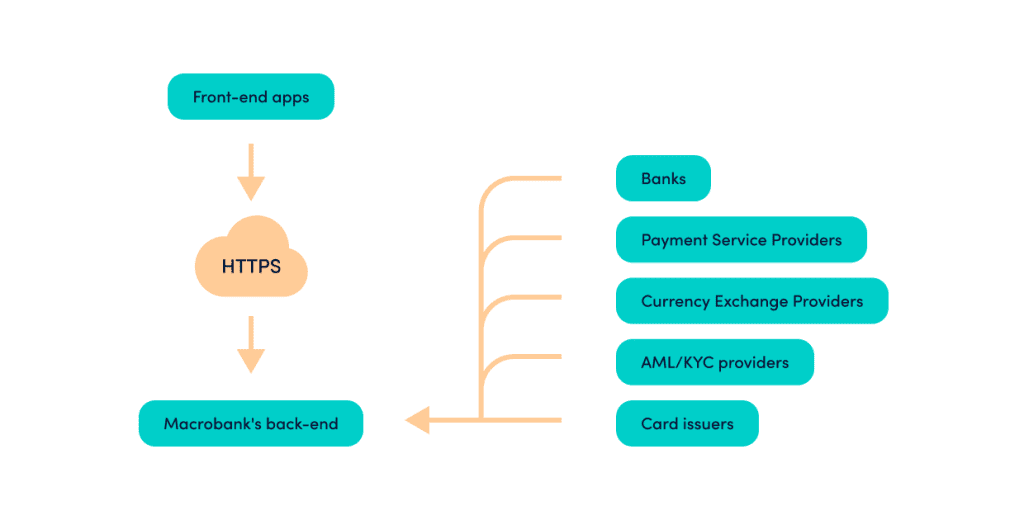
One prominent example of Banking as a Service (BaaS) in action is the partnership between a non-licensed fintech startup without its payment infrastructure and a licenced e-money institution or a bank (a BaaS provider). To connect to a BaaS provider, the fintech startup must sign an agreement with the provider and undergo compliance onboarding. After finalising the legal part, the fintech startup must do all the technical work. To connect to a BaaS provider’s API, the fintech startup must have a core banking system, e.g., Macrobank and a technical team.
Key characteristics and benefits of Banking as a Service
API-driven approach: BaaS relies heavily on APIs, rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate and interact. Through these APIs, non-banking (non-licensed) companies or companies without developed payment/banking infrastructure can securely access and utilise banking functionalities.
Product Offerings
Through BaaS, other licenced or non-licensed entities can offer a range of financial products and services, including payments, current accounts, currency exchange, card issuing, AIS, PIS, and more. These services are needed to be integrated into the core banking platform of a BaaS user.
Modularity
BaaS enables the modular approach to banking services. Companies can choose specific banking/payment services to integrate into their platforms, tailoring the offerings to suit their customer base. Also, BaaS enables the connection of different BaaS providers simultaneously. You need to have a flexible core banking platform to connect these providers.
Customer experience
By incorporating banking services directly into their products, companies can enhance their customer experience and streamline financial transactions, avoiding customers switching between different applications or websites.
Regulatory compliance
Since BaaS providers are established and licenced financial institutions, they already have the necessary regulatory approvals and compliance procedures. This allows non-regulated companies to leverage these capabilities without navigating complex regulatory frameworks and obtaining their own licence.
Partnerships and collaborations
BaaS encourages collaborations between banks and fintech companies, fostering an environment of innovation and efficiency in the financial industry.
Faster time to market: BaaS solutions can significantly reduce the time and cost required to develop and launch new financial products and services, enabling businesses to be more agile and responsive to market demands.
Evolution of BaaS
The concept of Banking as a Service (BaaS) has evolved over the years as advancements in technology, changes in consumer behaviour, and regulatory developments have shaped the financial services industry. Here is an overview of the evolution of BaaS:
Emergence of APIs
The foundation of BaaS lies in the development and adoption of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. APIs allowed different software systems to communicate and interact with each other, enabling seamless data sharing and integration of services.
Rise of Fintech
The emergence of fintech startups in the early 2000s brought increased innovation to the financial sector. Fintech companies leveraged APIs to create new financial products and services, leading to the integration of banking functions into non-banking platforms.
Open Banking Initiatives
Several countries introduced open banking regulations that mandated traditional banks to open their APIs to third-party developers. Open banking encouraged collaboration between banks and fintech firms, laying the groundwork for BaaS solutions.
Shift in Consumer Expectations
With the rise of digital technology, consumers began to expect seamless and personalised financial experiences. BaaS allows businesses to meet these expectations by embedding financial services directly into their products and platforms.
Evolving and tightened Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory frameworks have played a crucial role in shaping the BaaS landscape. While open banking regulations facilitated data sharing, other financial regulations, such as PSD2 in Europe and the coming PSD3 and new PSR, provided a framework for secure and standardised BaaS implementations. Moreover, as obtaining a licence becomes increasingly challenging, companies seek alternative opportunities to offer payment services to their customers.
Expansion of BaaS Providers
Traditional banks, recognising the potential of BaaS, started to offer banking infrastructure services to non-banking companies. Established technology companies also entered the BaaS market, offering turnkey solutions to businesses.
Modularity and Customisation
BaaS evolved to provide modular and customisable solutions, allowing businesses to select specific banking components to suit their unique requirements. This flexibility facilitated faster time-to-market for new products and services.
Global Adoption
BaaS gained traction worldwide as businesses across various industries realised the benefits of integrating financial services seamlessly into their platforms. Startups, established companies, and governments explored BaaS to enhance their offerings.
Security and Compliance Enhancements
As BaaS exchanges sensitive financial data, security and compliance became paramount. BaaS providers invested heavily in robust security measures and ensured compliance with data protection regulations.
Types of BaaS or Embedded Finance services
Here are some common types of BaaS services:
Current Accounts Creation and Management
BaaS enables the generation of IBANs and the creation and management of current accounts.
Digital Wallets
BaaS supports digital wallet integrations, allowing users to securely store and manage payment methods.
Foreign Exchange Services
Some BaaS providers offer foreign exchange capabilities, enabling businesses and their customers to perform currency conversions.
Card Issuance and Management
BaaS facilitates issuing and managing plastic and virtual debit cards, and other payment cards directly from the platform.
Bill Payments and Remittances
BaaS allows businesses and individuals to pay in different currencies and make international remittances seamlessly.
Open Banking Solutions
BaaS can facilitate open banking initiatives, where financial data can be securely shared between authorised parties to create innovative financial products and services – e.g., Payment Initiation Services (PIS) and Account Information Services (AIS).
Payment Processing
BaaS allows businesses to integrate payment processing capabilities, such as accepting credit card payments, facilitating peer-to-peer transfers, and handling electronic fund transfers.
What is the difference between Banking as a service and Open banking
Banking as a Service refers to a collaborative model that enables non-banking entities, such as fintech companies, e-commerce platforms, and other businesses, to offer their customers banking or payment services without becoming licenced institutions or without having own payment infrastructure. BaaS is based on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), facilitating seamless integration between traditional banks, licenced payment or e-money institutions and third-party providers.
On the other hand, Open Banking is a regulatory initiative that mandates financial institutions to share customer data with authorised third-party providers through APIs securely. Open Banking aims to promote competition, innovation, and better customer outcomes by empowering customers to share their financial data with trusted third-party providers.
BaaS focuses on enabling non-banking entities to provide banking services. In contrast, Open Banking empowers customers to share their data for personalised financial services securely.
How to Get Started with BaaS
By following these steps, you can start incorporating Banking as a Service into your platform and provide enhanced financial services to your customers. Advapay can guide you throughout the entire process, assisting you from start to finish. This includes helping you choose a BaaS provider from our partner network, providing a core banking solution Macrobank and facilitating the integration of a core banking solution with your selected BaaS partner.
1 – Identify Customer Needs
Before integrating more financial services into your platform, it’s essential to understand your customers’ requirements. Conduct user research to pinpoint their pain points and determine which financial services best address their needs.
2 – Select Suitable BaaS Providers
Ensure that your chosen BaaS provider offers services that align with your customer’s demands. Verify that the BaaS provider covers the regions and industries relevant to your client base.
3 – Undergo onboarding and AML process with your BaaS provider
Establishing a robust relationship relies heavily on a strong compliance understanding between both companies. Compliance often becomes a critical factor. During this process, ensure you have prepared to furnish the necessary legal, operational, and other documentation as required. Afterward, these documents are presented to regulatory bodies for their endorsement. Generally, this entire procedure spans a duration of approximately 2 to 3 months until finalization.
4 – Choose a Core Banking Platform
As most BaaS providers primarily offer APIs, you must be prepared to integrate these APIs with your core banking system. Select a core banking platform that suits your business model and complements the BaaS services you plan to offer. This platform will serve as the foundation for integrating the various BaaS services.
5 – Ensure a secure integration with BaaS providers
Achieve seamless connectivity of all BaaS services to establish a cohesive and fully functional system. Collaborate with the project management team of your core banking provider, who will assist you in linking your core banking platform with the embedded banking products, ensuring a smooth conversion process. If your core banking provider already offers ready integrations with various BaaS providers, you can save valuable time and effort.
Banking as a Service is transforming the financial industry, offering a win-win situation for traditional banks, licenced fintech institutions, and startups. Fintech companies, startups, and other businesses can rapidly expand their service offerings and gain a competitive edge in the market. At the same time, the banks and other liceenced institutions can diversify its revenue streams and stay relevant in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Advapay, a versatile core banking platform provider, presents an enticing opportunity to select a BaaS partner from a diverse range of readily integrated options for your business. Explore the compelling BaaS propositions offered by Advapay and discover the extensive list of available BaaS providers on our Marketplace page.
Book a call with our team!